Kt Kingtronics Diode & Rectifier List
3 Oct 2011| Diode Rectifier | |
| Diode M7 DO-214AC (1A 1000V) T&R RoHS. SMA | Diode SR560 (5A 60V) Bulk RoHS. DO-27 |
| Diode LL4148 SMD T&R RoHS. Minimelf | Diode UF4004 (1А 400V) Bulk RoHS. DO-41 |
| 1N4001-1N4007 | Diode UF4007 (1A 1000V) Bulk RoHS. DO-41 |
| 1N4001S-1N4007S | Diode 10A10 (10A 1000V) TO-R6 RoHS R-6 |
| 1N5400-1N5408 | Diode 1A7 (1A 1000V) Bulk RoHS R-1 |
| 1N5391-1N5399 | Diode 1N4007 (1A 1000V) Bulk RoHS DO-41 |
| RL201-RL207 | Diode 1N4148 (150mА 100V) Bulk RoHS |
| FR101-FR107 | Diode 1N4448 Bulk RoHS DO-35 |
| 1N4933-1N4937 | Diode 1N4937 Bulk RoHS DO-41 |
| FR151-FR157 | Diode 1N5397 (1,5A 600V) Bulk RoHS DO-15 |
| FR201-FR207 | Diode 1N5399 (1,5A 1000V) Bulk RoHS DO-15 |
| FR301-FR307 | Diode 1N5408 (3A 1000V) Bulk RoHS DO-27 |
| 1N5817-1N5819 | Diode 1N5819 (1A 40V) Bulk RoHS DO-41 |
| 1N5820-1N5822 | Diode 1N5822 (3A 40V) Bulk RoHS DO-27 |
| 6A05-6A10 | Diode 6A10 (6A 1000V) Bulk RoHS. R-6 |
| 1N5230B | Diode EM518 (1A 2000V) Bulk RoHS DO-41 |
| BZV55 | Diode FR207 (2A 1000V) Bulk RoHS. DO-15 |
| BZV55-C4V3 | Diode FR307 (3A 1000V) Bulk RoHS DO-27 |
| BZV55-C10 | Diode HER208 (2A 1000V) Bulk RoHS DO-15 |
| RS1M | Diode HER305 (3А 400V) Bulk RoHS DO-27 |
| Diode 1N5406 (3A 600V) Bulk RoHS. DO-27 | Diode HER307 (3А 800V) Bulk RoHS DO-27 |
| Diode 1N5407 (3A 800V) Bulk RoHS. DO-201AD | Diode SS16 (1A 60V) T&R RoHS. SMA |
| Diode FR157 (1,5A 1000V) Bulk RoHS. DO-15 | Diode SS14 (1A 40V) T&R RoHS. SMA |
| Diode FR607 (6A 1000V) Bulk RoHS. R-6 | Diode SF18 (1A 600V) Bulk RoHS. DO-41 |
| Diode HER102 Bulk RoHS. DO-41 | Diode SF26 (2A 400V) Bulk RoHS. DO-15 |
| Diode HER107 Bulk RoHS. DO-41 | Diode SF28 Bulk RoHS. DO-15 |
| Diode HER108 (1A 1000V) Bulk RoHS. DO-41 | Diode SF34 (3A 200V) Bulk RoHS. DO-201AD |
| Diode HER203 (2А 200V) Bulk RoHS. DO-15 | Diode SF36 (3A 400V) Bulk RoHS. DO-27 |
| Diode HER302 (3А 100V) Bulk RoHS. DO-27 | Diode SR360 (3A 60V) Bulk RoHS. DO-27 |
| Diode LL4448 SMD MINIMELF Tape & Reel RoHS | Diode SR506 (5A 60V) Bulk RoHS. DO-27 |
| Diode SB360 (3А 60V) Bulk RoHS. DO-27 | Diode SR510 (5A 100V) Bulk RoHS. DO-27 |
| Diode SB560 (5А 60V) Bulk RoHS. DO-27 | Diode SR540 (5А 40V) Bulk RoHS. DO-27 |

Bridge rectifiers and zener diodes are commonly used in electronic products such as computers and stereos. Bridge rectifiers are composed of a four-diode array.
These diodes convert alternating current into direct current. Bridge rectifiers have four leads, and are found in power supplies. Zener diodes are used to provide
regulated voltage for power supplies. A failure of either a bridge rectifier or zener diode prevents electronic devices from working properly.
- Unplug the device that contains the bridge rectifier. This ensures the bridge rectifier is without power.
- Set the digital multimeter, or DMM, to the "diode test" setting per the device's instructions.
- Test the bridge rectifier diodes. Place the DMM's two leads on two adjacent rectifier pins. The DMM will read either "OL," indicating an open circuit; or a voltage of 0.7 volts DC or less. Switch the DMM leads. An operational bridge rectifier diode shows a reading opposite of the previous reading. Perform this test on each adjacent pair of bridge rectifier pins. The bridge rectifier is faulty if the readings are the same for any of the individual diodes.
- Unplug the device containing the zener diode. This ensures the zener diode has no power.
- Set the DMM to the "diode test" setting.
- Test the zener diode. Place the two DMM leads on the two zener diode leads. The DMM will read either "OL" or 0.7 volts DC. Switch the DMM leads. A working zener diode exhibits a second reading opposite of the first reading.

Kt Kingtronics Uses of Zener Diodes
11 Jul 2011Since the voltage dropped across a Zener Diode is a known and fixed value, Zener diodes are typically used to regulate the voltage in electric circuits. Using a resistor to ensure that the current passing through the Zener diode is at least 5mA (0.005 Amps), the circuit designer knows that the voltage drop across the diode is exactly equal to the Zener voltage of the diode.
NEW Click here to visit Zener-Diode.co.uk for a site dedicated to zener diodes, their characteristics, usage, and other information.
Zener Diode Voltage Regulator Circuit
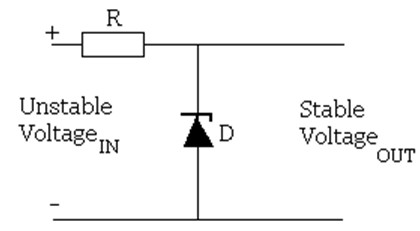
A zener diode can be used to make a simple voltage regulation circuit as pictured above. The output voltage is fixed at the zener voltage of the zener diode used and so can be used to power devices requiring a fixed voltage. Click here to find out more about the Zener Diode Voltage Regulator and how you go about selecting the resistor and zener diode.
NEW The above mentioned article on zener diode voltage regulators has now been updated and a handy calculator has been added to help you select the correct resistor and zener diode values and power ratings.
Zener Diodes in Series With Loads
If you have a regulated fixed voltage - say 12 Volts from a desktop PC power supply, and you want to power something requiring a lower voltage, it is possible to simply place a zener diode in series with the load device. You would choose a diode with a zener voltage equal to the supply voltage minus the voltage drop across the load.

For example, if you have a 1 Watt 6 Volt lightbulb to power from a 12 Watt regulated power supply, a 6.2V zener diode could be placed in series with the bulb giving the bulb 5.8V, or you could overpower the bulb a little using a 5.6V zener diode and dropping 6.4V across the bulb. Heat would be generated in the zener diode so it is essential to calculate the power lost in it so a suitably rated diode could be chosen.
Using a 5.6V zener diode, and knowing the bulb draws a current of around one-sixth of an Amp, we can calculate the power loss in the diode (with Ohm's Law) to be just under 1 Watt. Therefore a standard 1.3 Watt zener diode should be up to the job.
Circuits with Zener Diodes
Zener diodes are key components in the circuits presented in the following articles: Make a Simple Battery Status Monitor, LM741 Voltage Indicator, and High Capacity Alternative to 9V Battery.
Kt Kingtronics Rectifier's Application
29 Nov 2010Rectifiers find a use in detection of amplitude modulated radio signals. The signal may be amplified before detection, but if un-amplified, a very low voltage drop diode must be used. When using a rectifier for demodulation the capacitor and load resistance must be carefully matched. Too low a capacitance will result in the high frequency carrier passing to the output and too high will result in the capacitor just charging and staying charged.
Kingtronics’s fast recovery rectifier diodes are very popular in the overseas market, According to the rectifier’ s application , Our Kingtronics managing ordinary rectifier diodes, ultra-fast rectifier diodes. In our Kingtronics website www.kingtronics.com ,we have detailed PDF about all kinds of diodes & rectifiers.
- 0Commentary
- Tags:Kt Kingronics Kt fast response rectifier diodes Kt High ripple current Aluminum Elec capacitors Bridge rectifiers appreciating chrysanthemum business cooperation Chip multilayer ceramic capacitors Communications Equipment Equipment Manufacturers Passive Electronics Components The supply voltage trimmer potentiometers Zener Diodes
Contact us
Tel: (86) 769 8118 8110
Tel: (852) 8106 7033
Fax: (852) 8106 7099
E-mail: info@kingtronics.com
Skype: kingtronics.sales
MSN: kingtronics-sales@hotmail.com
Web: www.Kingtronics.com
YouTube: www.youtube.com/c/Kingtronicskt
About
Kingtronics International Company was established in 1995 located in Dongguan City of China to handle all sales & marketing for factories located in Chengdu, Sichuan and Zhaoqing, Guangdong, China. In 1990, we established the first factory to produce trimming potentiometer and in 1999 we built up new factory in Zhao Qing, Guangdong. Now with around 850 workers, Kingtronics produce trimming potentiometers, dipped tantalum capacitors, multilayer ceramic capacitors, and diode & bridge rectifier. We sell good quality under our brand Kingtronics, and Kt, King, Kingtronics are our three trademarks. All our products are RoHS compliant, and our bridge rectifier have UL approval. Please visit our Products page, you could please download all our PDF datasheet and find cross reference for our Trimming Potentiometer and capacitors.
Tantalum and Ceramic Capacitors Cross Reference ↓ Download
Diodes & Rectifiers List(PDF: 97KB) ↓ Download
Trimming Potentiometer Cross Reference ↓Download
Categories
- Kt Kingtronics (245)
- Diodes & Rectifiers (160)
- Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor (149)
- Trimming Potentiometers (123)
- Tantalum Capacitors (94)
- Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors (70)
- Kt Bridge Rectifier (64)
- Quartz Crystals (58)
- Surge Arresters (34)
- Tactile Switches (32)
- Kt Kingtronics Components (30)
- Ceramic Trimmer Capacitors (25)
- Film Capacitors (23)
- Super Capacitors (17)
- Metal Oxide Varistor (10)
- Negative Temperature Coefficient Thermistor (6)
- Music capacitors (2)
Archives
- 2024 April (3)
- 2024 March (2)
- 2024 February (2)
- 2024 January (3)
- 2023 December (1)
- 2023 November (2)
- 2023 October (1)
- 2023 September (2)
- 2023 August (2)
- 2023 July (4)
- 2023 June (12)
- 2023 May (6)
- 2023 April (4)
- 2023 March (3)
- 2023 February (2)
- 2023 January (1)
- 2022 December (3)
- 2022 November (2)
- 2022 October (3)
- 2022 September (4)
- 2022 August (3)
- 2022 July (3)
- 2022 June (2)
- 2022 May (3)
- 2022 April (4)
- 2022 March (4)
- 2022 February (2)
- 2022 January (3)
- 2021 December (4)
- 2021 November (3)
- 2021 October (4)
- 2021 September (4)
- 2021 August (4)
- 2021 July (4)
- 2021 June (5)
- 2021 May (4)
- 2021 April (3)
- 2021 March (4)
- 2021 February (4)
- 2021 January (4)
- 2020 December (5)
- 2020 November (4)
- 2020 October (4)
- 2020 September (7)
- 2020 August (8)
- 2020 July (9)
- 2020 June (8)
- 2020 May (9)
- 2020 April (11)
- 2020 March (6)
- 2020 February (4)
- 2020 January (4)
- 2019 December (6)
- 2019 November (7)
- 2019 October (6)
- 2019 September (5)
- 2019 August (9)
- 2019 July (6)
- 2019 June (4)
- 2019 May (16)
- 2019 April (6)
- 2019 March (6)
- 2019 February (9)
- 2019 January (5)
- 2018 December (4)
- 2018 November (4)
- 2018 October (5)
- 2018 September (8)
- 2018 August (10)
- 2018 July (7)
- 2018 June (12)
- 2018 May (22)
- 2018 April (4)
- 2018 March (4)
- 2018 February (8)
- 2018 January (13)
- 2017 December (4)
- 2017 November (4)
- 2017 October (5)
- 2017 September (4)
- 2017 August (21)
- 2017 July (7)
- 2017 June (5)
- 2017 May (4)
- 2017 April (4)
- 2017 March (9)
- 2017 February (8)
- 2017 January (8)
- 2016 December (10)
- 2016 November (16)
- 2016 October (8)
- 2016 September (10)
- 2016 August (13)
- 2016 July (12)
- 2016 June (10)
- 2016 May (14)
- 2016 April (8)
- 2016 March (10)
- 2016 February (6)
- 2016 January (8)
- 2015 December (10)
- 2015 November (8)
- 2015 October (3)
- 2015 July (5)
- 2015 June (9)
- 2015 May (7)
- 2015 April (8)
- 2015 March (9)
- 2015 February (7)
- 2015 January (5)
- 2014 December (13)
- 2014 November (4)
- 2014 October (4)
- 2014 September (5)
- 2014 August (4)
- 2014 July (4)
- 2014 June (4)
- 2014 May (4)
- 2014 April (4)
- 2014 March (5)
- 2014 February (3)
- 2014 January (4)
- 2013 December (8)
- 2013 November (9)
- 2013 October (10)
- 2013 September (9)
- 2013 August (11)
- 2013 July (10)
- 2013 June (3)
- 2013 May (4)
- 2013 April (5)
- 2013 March (2)
- 2013 February (1)
- 2013 January (3)
- 2012 December (5)
- 2012 November (6)
- 2012 October (5)
- 2012 September (10)
- 2012 August (11)
- 2012 July (11)
- 2012 June (12)
- 2012 May (14)
- 2012 April (10)
- 2012 March (14)
- 2012 February (10)
- 2012 January (6)
- 2011 December (9)
- 2011 November (11)
- 2011 October (10)
- 2011 September (13)
- 2011 August (14)
- 2011 July (13)
- 2011 June (13)
- 2011 May (13)
- 2011 April (14)
- 2011 March (27)
- 2011 February (13)
- 2011 January (24)
- 2010 December (21)
- 2010 November (12)
- 2010 October (11)
